Protection against Fraud and Identity Abuse
| Site: | Soteria H2020 awareness training |
| Course: | E-training for personal data management and privacy |
| Book: | Protection against Fraud and Identity Abuse |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 10 March 2026, 7:19 AM |
1. Why is it important?
Tasks such as shopping, banking or dealing with the authorities are increasingly being carried out online. In the process, sensitive data such as passwords or payment data must be disclosed. It is therefore important for users to be able to recognize fraud attempts and protect themselves accordingly.
Reputable companies encrypt data exchange and offer secure payment methods.
Criminals with fraud intentions try to spy on these passwords and payment data. They request sensitive information in various ways and misuse it.
And there are other fraudulent methods.
Phishing emails, fraudulent free offers, fake winning notifications, ransomware, love scams, insecure apps, value-added SMS, and subscription traps are among the most common types of Internet fraud.
You can also get more detailed information about current scams here:
Online Threat Alerts (OTA) - Web, Internet and Cyber Threats
2. How do I do it?
There are several things you can do to protect yourself from fraud and identity abuse on the Internet.
- Be wary of offers that are unusually cheap. Compare prices. Find out what other customers and clients are saying about a provider on the Internet. If there are predominantly negative or no reviews about an online store, you should shop elsewhere.
- Pay attention to any seals of approval or association memberships on the seller's website. For example the Austrian E-Commerce Quality Seal identifies reputable online stores that have been tested for quality, customer-friendliness and security.
- Avoid payments in advance by bank transfer. Use secure means of payment and, in the case of auctions, also trust systems. For purchases from private individuals, insist on a personal handover - if possible.
- Use strong passwords: Use a strong password for each account.
- Update your software: Make sure your computers and mobile devices are updated with the latest security updates. This will help close known security holes and protect you from malware and other threats.
- Be careful about sharing information: Never give out personal or financial information such as credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, or passwords to people you meet online or don't know.
- Use only secure websites: Make sure the websites you visit start with https. This means the site uses a secure connection and your information is encrypted during transmission.
- Check your bank and credit card statements regularly to identify and quickly respond to unauthorized transactions.
- Be careful with emails and attachments: Do not open emails or attachments from people you do not know.
- Be wary of emails that claim to be from your bank or another company and ask you to disclose personal information or click on a link.
- Use two-factor authentication wherever possible. This requires an additional security code to access your accounts, making it harder to access your data.
- Use antivirus software on your computers and mobile devices to detect and remove malware.
- Use public Wi-Fi with caution, as it's easy for hackers to intercept your data. Use a VPN to encrypt your connection and protect your data.
2.1. Secure connection
Secure connection during data transmission means that the data is protected during transmission and cannot be intercepted or manipulated by third parties. A secure connection is usually achieved by encrypting the data.
There are several methods to establish a secure connection, including SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) for encrypting web connections, VPN (Virtual Private Network) for secure connection between remote networks or devices, and SSH (Secure Shell) for secure remote control of computers.
A secure connection is especially important when transferring sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card information, or other personal data. Without a secure connection, such information can be intercepted and stolen by attackers.
Therefore, make sure you have a secure connection and check the certificate.
You can recognize a secure connection by https in the web address.
Example of a secure connection:
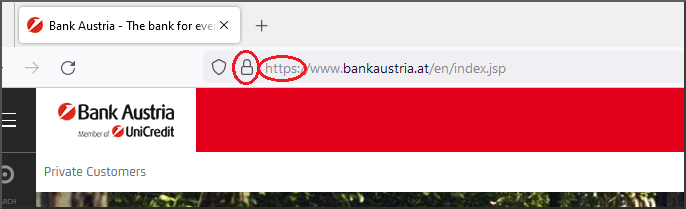
You can access and verify the certificate via the lock icon.
A website's certificate is a digital document issued by a trusted certification authority that verifies the identity of the website. It contains information such as the name of the website, the name of the issuing certification authority, the purpose of the certificate, and the validity period of the certificate. The certificate also contains a public key that is used to encrypt data.
The certificate is provided by the website and can usually be verified by clicking the lock icon in the browser's address bar. If the certificate is valid, a secure connection is established and all data exchanged between the user's browser and the website is encrypted.
A certificate ensures that the website displayed is indeed the one mentioned in the address bar, and that data is transmitted in encrypted form.
When a user accesses a website that does not have a valid certificate, a warning message is usually displayed, indicating that the connection may not be secure. In this case, users should be careful and not visit the website unless they are sure that the website is legitimate and that the data they are transferring is not confidential.
2.2. Recognize phishing
Phishing is a form of cyber attack in which fraudsters attempt to steal sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers or bank details. This is often done through fake emails that look like they come from a trusted company, such as a bank or delivery service, in order to trick the recipient into clicking on a link and entering their details on a fake website. Do not click on such links! If you just point at such a link with your mouse, in most cases you can see that the link leads to a completely different website.
Smishing: In this form of phishing, a text message is used to trick the victim into clicking on a link or visiting a fake website.
Vishing: This involves contacting the victim by phone and trying to get them to give up their details. The caller often poses as an employee of a bank or other company.
Examples of phishing e-mails
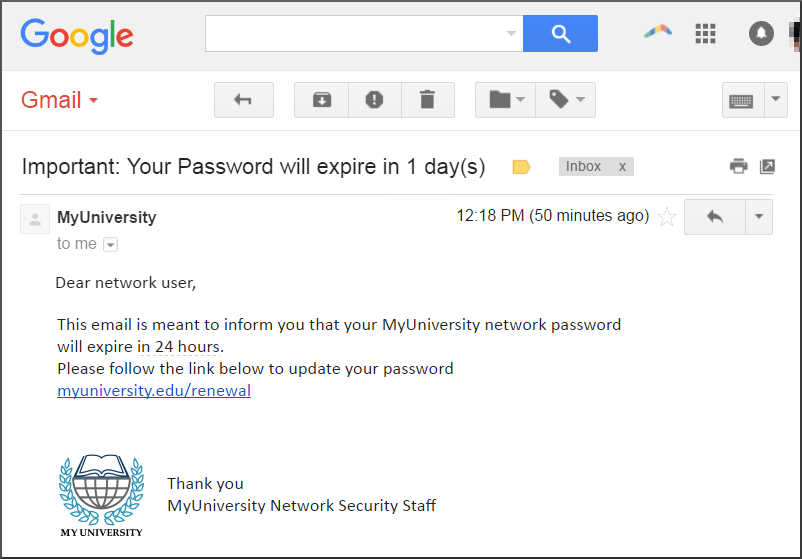
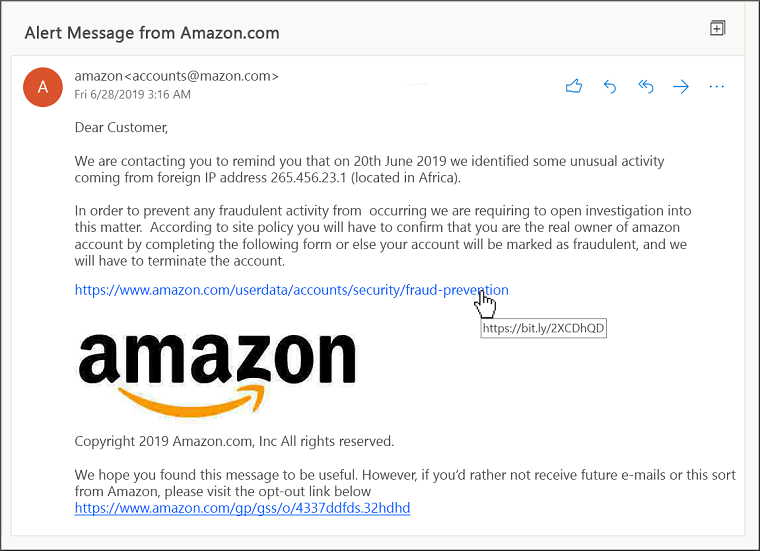
2.3. As a victim, what can I do?
If you have been the victim of a cybercrime incident, there are a number of steps you can take to manage your situation and minimize the damage. Here are some important steps you should take:
- Notify law enforcement: Report the incident to local police or other appropriate authorities. Provide all relevant information, including details of the incident, any known perpetrators or suspicious activity
- Preserve evidence: Take screenshots, copy emails or other digital evidence documenting the incident. This evidence can be useful later in an investigation or legal action.
- Change your passwords: if you suspect your accounts have been compromised, change all affected passwords immediately. Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication when available.
- Notify your bank and credit card companies: If financial information is affected, contact your bank and/or credit card companies immediately to report suspicious activity and potentially block cards or reverse transactions.
- Review your account activity: Carefully review your bank and credit card statements, online accounts and other financial transactions to identify unauthorized activity. Report suspicious incidents immediately.
- Report the incident to the appropriate organizations: Cybercrime can impact multiple areas. Report the incident to the appropriate agencies, such as your Internet service provider, your email service provider, or the social media platforms on which you are active.
- Check your computer and network security: run comprehensive virus scans on your computers and other devices to detect any malware or other harmful programs. Update your operating systems, applications and antivirus programs to the latest versions.
- Consider contacting experts: If the incident is serious or you are having difficulty coping with the damage, consider contacting experts such as lawyers, IT security specialists or victim assistance organizations. They can help you deal with the incident and restore your security.
It is important to act quickly to minimize the damage and avoid further risk. Every incident is unique, and the exact steps may vary depending on the type of cybercrime incident.
3. Further explanations
This chapter provides further explanations on specific topics.
Please select from the table of contents on the right.
3.1. Legal notice
In Austria, due to several legal provisions, there is a so-called "imprint obligation" or obligation to provide a legal notice for websites.
Based on the legal notice, you can draw conclusions about the trustworthiness of a website.
This is because information about the website must be disclosed in the legal notice. For commercial websites with an online store, for example, the following information must be provided:
- The name of the online store operator or their company
- The geographical address at which the company is established
- Information enabling users to contact the online store operator quickly and directly and their e-mail address
- If available, the company register number and the company register court
- If the activity is subject to official supervision, the competent supervisory authority
- In the case of online store operators who are subject to trade or professional regulations, the chamber, professional association or similar institution to which the online store operator belongs
- Professional title and Member State in which the professional title was awarded
- Reference to the applicable trade or professional regulations and also an access to these regulations
- If available, sales tax identification number
- Location of the business license, if the company is not registered in the commercial register
Often the link to the legal notice is located at the bottom of the web pages.
Examples of imprint:
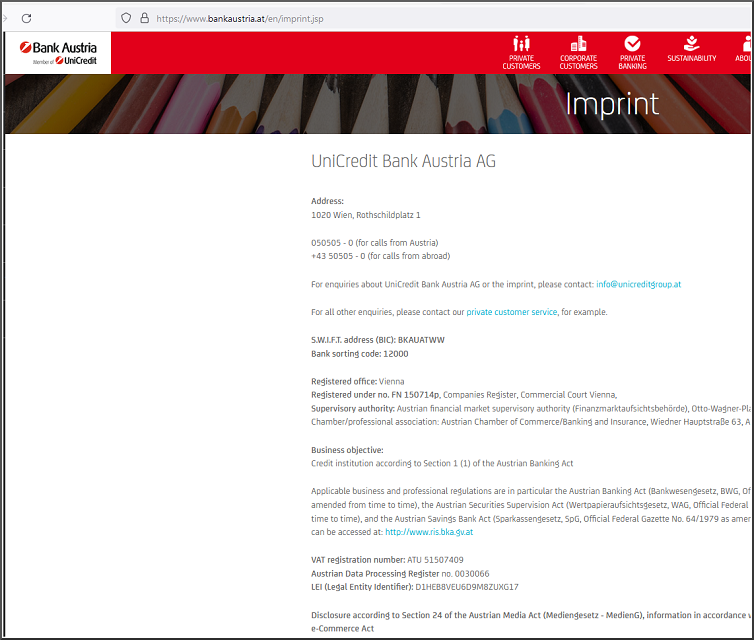
3.2. Links to websites with further information
Listed below are links to websites with more information:
Online Threat Alerts (OTA) - Web, Internet and Cyber Threats
European Consumer Centre Austria | Advice and assistance for consumers in Europe
3.3. Online shopping fraud and identity theft
Fraudsters create fake online stores that offer high-quality products at very low prices. They take payments, but either deliver low-quality products or do not deliver anything at all. Victims lose their money and do not receive any goods.
These fake stores often look deceptively genuine and offer high-quality products at extremely low prices to attract potential buyers. The fraudulent merchants often invest a lot of time and effort to make their fake websites look professional. They use pictures and descriptions of real products to gain buyers' trust.
When a customer places an order and pays for the purchase, the fraudsters receive the money. This is followed by no delivery, or delivery of inferior or fake goods.
In some fraudulent online stores, customers are asked to enter personal information such as credit card details, social security numbers or addresses. This information can subsequently be used by the fraudsters for identity theft and other fraudulent purposes.
There are also known cases where fraudsters have manipulated legitimate online stores, for example, redirects for the payment process are manipulated. Therefore, it is important to check whether a redirect to the correct payment service is made.
3.4. Online dating scam
Online dating scams occur when fraudsters on dating platforms try to gain the attention and trust of other users. Fraudulent goals include financial gain, identity theft, or emotional manipulation. Here are some examples:
- Romantic scam: Scammers pretend to fall in love with their potential victim by using fake profiles and establishing an intense online relationship. Once an emotional connection is established, they often ask for financial assistance by pretending to be in financial trouble or have urgent medical expenses.
- Identity theft: In some cases, scammers use online dating platforms to collect personal information from victims. This information can be used for identity theft and other fraudulent activities.
- Catfishing: Scammers may use fake profiles to impersonate another person, often celebrities or attractive people. They use these fake identities to deceive people, collect personal information, or manipulate people emotionally.
3.5. Sexting
Sexting refers to the exchange of intimate, sexually explicit messages, pictures or videos over the Internet. Of course, this can take place consensually between the people involved. However, there are also cases where sexting has undesirable consequences and/or is also punishable. Here are some examples:
- Sextortion: scammers can use sexting messages or pictures to blackmail their victims. They threaten to publish the intimate content or send it to friends and family unless the victim pays money or complies with their demands.
- Dissemination without consent: In some cases, a person who has been involved in sexting shares the intimate content they have received without the other person's consent. This can lead to embarrassing or harmful situations and violate the privacy and well-being of the person involved.
Such dissemination is punishable by law, as is the dissemination of explicit content from minors.
In this context, consider possible risks. Above all, that you lose control over content shared on the internet.