Personal Data and Privacy Protection.
| Site: | Soteria H2020 awareness training |
| Course: | E-training for personal data management and privacy |
| Book: | Personal Data and Privacy Protection. |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Sunday, 18 January 2026, 7:02 AM |
1. Why is it important?
By identifying our devices, via apps and with the help of cookies, data about our behavior and preferences is collected. This enables personalized advertising, but also discrimination and manipulation. In this context, examples from the recent past also point to socio-political dangers.
Personal data is information about an individual that can be used to identify them, such as their name, address or date of birth. Privacy refers to a person's ability to protect their personal information from unauthorized access and use.
Privacy protection allows each person to control how their personal information is collected, used, and shared. This can prevent misuse of personal information.
In our increasingly digital world, privacy also ensures the preservation of personal freedom, security and autonomy.
If you would like to learn more about a specific topic, please select the appropriate topic from the table of contents on the right.
1.1. Data worth protecting
If you want to protect your privacy, it is first necessary to define in which cases it is data worth protecting.
Basically, data that is worth protecting is data that can cause damage if misused, either on its own or by linking it to other data. This can be personal data (e.g. PIN, TAN, health data, ...) or factual data (e.g. setting for alarm system, company secrets, ...).
More detailed information is also available here: Information privacy - Wikipedia
1.2. Handling of personal data
Many people are willing to share personal data with service providers and companies in exchange for adequate benefits, such as free email accounts, discounts, unlimited cloud storage, and so on.
You should only use services that you actually need, transmitting as little data as possible and limiting its disclosure.
You can also get more detailed information here: Information privacy - Wikipedia
1.3. Advertising, manipulation, discrimination
-
Personalized advertising and content: Companies and platforms collect data about users to provide personalized advertising and content. However, this can lead to users being trapped in filter bubbles where they only see certain information and opinions, while dissenting views are hidden. This can limit the diversity of opinions and achieve manipulation of perceptions of certain topics.
-
Price discrimination: By analyzing user data, companies can set different prices and offers based on individual profiles and behaviors. This can lead to price discrimination, where certain user groups have to pay higher prices for products or services while other groups receive preferential offers.
-
Job search and credit discrimination: When companies analyze applicant profiles based on user data, there is a risk of discrimination in job searches. For example, if information such as gender, age or ethnicity is included in the analysis, certain applicants could be disadvantaged. The same applies to lending, where data can be used to assess creditworthiness.
-
Manipulation of elections and political opinion: The collection of user data makes it possible to send targeted political messages to specific audiences. This can lead to political opinions being manipulated or amplified by targeting or distorting information to achieve specific political goals. The best-known example of this is the Cambridge Analytica scandal, in which the data of millions of Facebook users was misused for political purposes.
-
Surveillance and government control: Governments can use collected user data to monitor citizens, persecute political dissidents, or restrict civil liberties. This can lead to a climate of fear and self-censorship as people's privacy and freedom are compromised.
2. How do I do it?
You can protect your privacy through your behavior and appropriate settings in your devices and apps.
Cookies
You have the choice! You can refuse cookies or accept only necessary cookies.
The more cookies you accept, the more accurate the profile created about you.
Browser settings
You can protect your privacy with the following browser settings.
Private window After closing Private windows, cookies are cleared, for example.
Clear browser data on close You specify which data should be deleted when you close the browser.
Privacy settings on devices
Tracking Allow or deny tracking
Customize permissions for apps such as access to location, camera, microphone, photos, contacts.
2.1. Cookies
What is a cookie?
A cookie is a small text file that a website stores on a person's device (computer, smartphone, etc.) when they visit the website. The cookie is used to remember the user's preferences, login information, and other data that the website can use to personalize the user's experience. Cookies can be temporary (session cookies) or persist for an extended period of time (persistent cookies). Cookies are a common technology used by many websites to provide a better and more personalized browsing experience, to personalize advertising, but also to create accurate profiles of individuals. Subsequently, such profiles are often resold.
Cookies settings
Typically, you can:
Accept all
Accept only necessary cookies
Reject all
Accept selection only
Examples of choices
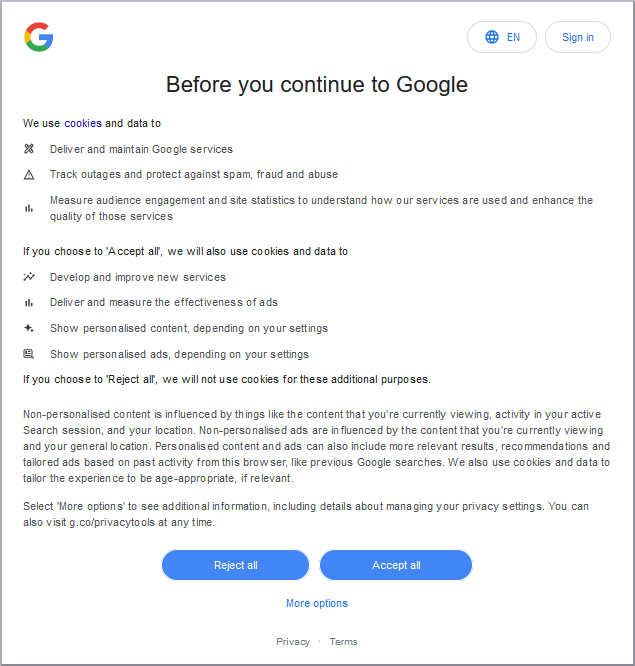
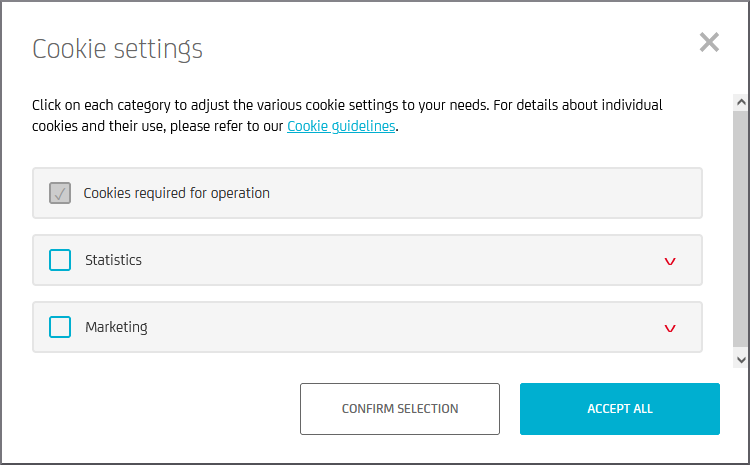
2.4. Backup your data
The operating systems Windows, ios, or Android offer you the possibility to store your data or parts of it in the respective cloud of the provider.
You can save your data on external media such as USB stick or external hard drive.
The most important principles of data backup can be summarized as follows:
- Regularity: data should be backed up regularly to ensure that current and important information is not lost. The frequency of backups depends on the type of data and how often it changes. It is advisable to set a fixed schedule for data backups.
- Redundancy: It is important to make multiple copies of the data and keep them in different locations. This ensures that an alternate copy of the data is always available in case of hardware failure, theft, or a disaster such as a fire.
- Verification: It is essential to regularly verify the integrity and recoverability of the backed up data. This ensures that the backups are functioning properly and that the data can be restored correctly if necessary.
- Security: backed up data should be protected from unauthorized access. This can be achieved through encryption techniques to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the data. Additionally, backup media should be stored securely to prevent theft or loss.
- Diversify: It is advisable to use different types of data backup technologies and media to protect data from various threats. This may include the use of cloud storage, external hard drives, tape drives or network storage. Diversifying backup methods reduces the risk of all copies of data being compromised at the same time.
- Documentation: it is important to maintain clear documentation of the data backup strategy. This documentation should include information on the schedule of backups, technologies used, locations, and responsibilities. This will ensure that the backup can be managed effectively and responded to quickly in the event of a failure.
These principles form the basic framework of an effective data protection strategy. By adhering to these principles, organizations and individuals can ensure that their data is protected and can be restored when needed.
3. Further explanations
This chapter provides further explanations on specific topics.
Please select from the table of contents on the right.
3.1. Privacy settings
You can activate privacy settings on your devices and adapt them to your needs. You have the option to individually change your settings in apps, operating systems, browsers, online services, social media accounts or search engines.
3.2. Location services
If you activate location services/location access, the current location of your device is determined via GPS and WLAN location. This means that your personal location can usually also be determined.
One location service, for example, is the Global Positioning System (GPS), but Wi-Fi location via the WLAN signal is also possible.
Activating location services on your smartphone has both advantages and disadvantages. Some of the main implications are:
Advantages:
- Improved navigation: location service allows you to navigate from one place to another quickly and easily.
- Better security: if your smartphone is stolen, you can locate it using the location service.
- Better personalization: Some apps use the location service to provide personalized recommendations and offers based on your location.
- More convenience: some features, such as automatic time zone adjustment, can be automatically enabled by the location service.
Disadvantages:
- Limitation of privacy: when location service is enabled, apps can track and record your location, which can affect your privacy.
- Increased battery consumption: location service can drain your smartphone battery faster.
- Data recording: when the location service is enabled, your location and related data may be recorded by your smartphone and potentially used by third parties.
- Third-party tracking: When the location service is enabled, your location may be tracked by third parties, which may cause security concerns.
3.3. Cloud services
Cloud services are online services that allow users to store and use files, applications, databases and other resources in an external cloud infrastructure. Instead of storing these resources on the user's local computer or server, they are stored on servers in a remote data center and made accessible over the Internet.
Cloud services offer a number of benefits. One of the most important benefits is the flexibility they offer. Since users can access their data and applications from any location with Internet access, they can work from any device, be it a computer, tablet or smartphone. Moreover, they can access their data anytime, anywhere as long as they have a connection to the Internet.
Another advantage of cloud services is that they are often scalable. Users can increase or decrease their usage as needed, depending on how much storage or processing power they need. This means they only have to pay for the resources they actually use, rather than paying for a fixed amount of storage or computing power.
In addition, cloud services often offer automatic backup and recovery options that can improve the security and availability of data and applications. Users don't have to worry about backing up and restoring their data, as these features are usually provided automatically by the cloud service.
Overall, cloud services offer a simple, flexible and scalable way to store and use data and applications, which can be beneficial for both home users and businesses.
Despite the many advantages, cloud services also have some disadvantages that should be considered. Some of the main disadvantages are:
- Dependence on internet connection: cloud services require a stable and fast internet connection to be used effectively. If the internet connection goes down or is unstable, it can cause delays or even complete loss of access to the data and applications.
- Data security: when data is stored on a cloud server, it is accessible to third parties, which increases the risk of data loss, theft or tampering. However, there are measures users can take to keep their data secure, such as using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication.
- Privacy: another issue related to cloud services is privacy. Some users are concerned that their personal data is stored on cloud servers and can be viewed by third parties or even government agencies.
- Cost-effectiveness: although cloud services are often scalable and flexible, they can be expensive in the long run, especially for companies that require large amounts of data or computing power.
- Limited control: when data is stored on a cloud server, users often have limited control over how that data is stored, backed up or restored. This can cause problems when it comes to meeting data protection or compliance requirements.
Overall, users should carefully weigh the pros and cons of cloud services before deciding to use them. If the advantages outweigh the disadvantages and appropriate security precautions are taken, cloud services can be a useful and effective way to store and use data and applications.
3.4. Terms
Clickbait, Clickbaiting
Clickbaiting (from click and bait) is a media-critical term for the practice of advertising content on the World Wide Web in order to achieve more page impressions and thus, among other things, more advertising revenue through Internet advertising, subscriptions to paid content behind a paywall or greater brand awareness of the target page or author.
A clickbait usually consists of a headline and a teaser that create a so-called curiosity gap. They tell the reader just enough information to make them curious, but not enough to satisfy that curiosity, similar to a cliffhanger. The headline can be supplemented or replaced by graphic elements with the same function.
The articles behind a clickbait are usually well equipped with facilities for quick sharing on social networks, which increases the access numbers as well.




